About Cervical Spondylosis
Cervical spondylosis refers to age-related wear and tear affecting the spinal disks in the neck. As disks dehydrate and shrink, signs of osteoarthritis can develop, including bony projections along bone edges. This common condition affects more than 85% of people over age 60, though many experience no noticeable symptoms.
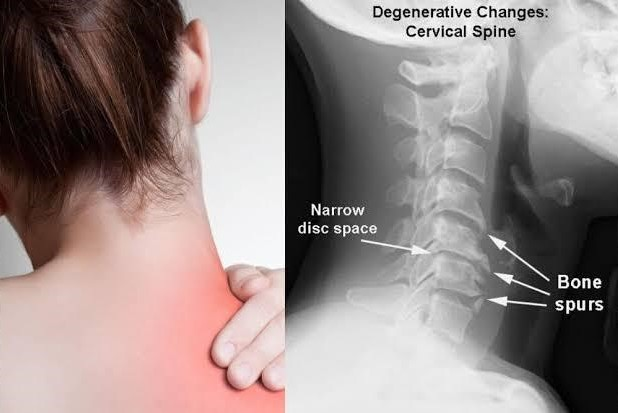
Common Indicators
Some people may experience:
- Neck stiffness or pain
- Headaches originating from the neck
- Grinding or popping sensations when moving the neck
- In some cases, numbness or weakness in limbs
Contributing Factors
Several elements may influence development:
- Natural aging processes
- Previous neck injuries
- Genetic factors
- Occupational activities requiring repetitive neck movements
- prolonged periods of sitting with poor posture
How to prevent and relieve cervical spondylosis?
Practical approaches for neck health include:
Posture and Movement Strategies
- Maintain neutral head position during daily activities
- Adjust computer screens to eye level
- Take regular breaks from prolonged sitting
- Practice gentle neck stretches throughout the day
Lifestyle Considerations
- Stay physically active with neck-friendly exercises
- Use supportive pillows during sleep
- Maintain healthy body weight
- Stay hydrated to support spinal disc health
Pain Management Approaches
- Apply heat or cold therapy for comfort
- Practice relaxation techniques to reduce muscle tension
- Consider over-the-counter pain relief after medical consultation
- Use proper ergonomic supports when working
Professional Care Options
- Consult healthcare providers for persistent symptoms
- Seek physical therapy for targeted exercises
- Consider professional massage or manual therapy
- Explore medical interventions if conservative methods prove insufficient
When to Seek Medical Advice
Consult healthcare professionals for:
- Severe or worsening neck pain
- Numbness or weakness in arms or hands
- Loss of bladder or bowel control
- Symptoms that disrupt daily activities
- Pain following injury or trauma
Long-Term Management
Cervical spondylosis management typically involves:
- Consistent attention to posture and movement habits
- Regular appropriate physical activity
- Ongoing communication with healthcare providers
- Adaptation of activities based on symptom changes
Prevention Strategies
While not all cases can be prevented, these practices may help:
- Regular neck-strengthening exercises
- Maintaining good posture during activities
- Using proper techniques when lifting objects
- Varying positions during prolonged activities
Cervical spondylosis represents a common aspect of aging that many people experience. While various management strategies exist, individual responses may vary. Professional medical guidance ensures appropriate diagnosis and personalized management plans. Remember that maintaining neck health involves consistent attention to movement patterns, posture, and overall physical activity throughout daily life.



