Introduction
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD), also known as ischemic heart disease, is the leading cause of death worldwide. It occurs when the coronary arteries—the blood vessels that supply oxygen-rich blood to the heart—become narrowed or blocked due to plaque buildup (atherosclerosis). This restricts blood flow, potentially leading to heart attacks, angina, or heart failure.
This article covers:
✔ What CAD is and how it develops
✔ Major risk factors
✔ Warning signs and symptoms
✔ Diagnosis and treatment options
✔ Prevention strategies
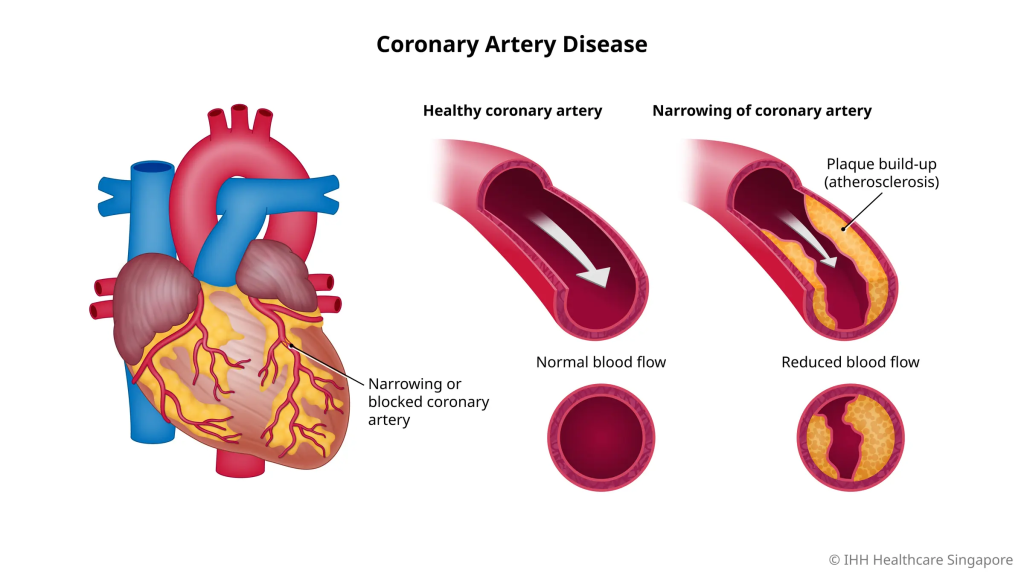
How Does CAD Develop?
CAD progresses gradually due to atherosclerosis—a buildup of cholesterol, fat, calcium, and other substances in the artery walls. Over time, this leads to:
🔴 Plaque formation → Narrowed arteries (stenosis)
🔴 Reduced blood flow → Heart muscle starvation (ischemia)
🔴 Plaque rupture → Blood clot formation → Heart attack
Key Risk Factors
Non-Modifiable Risks
- Age (Men >45, Women >55 at higher risk)
- Family history of heart disease
- Gender (Men are at higher risk, but women’s risk increases after menopause)
Modifiable Risks
✔ High blood pressure (damages artery walls)
✔ High LDL cholesterol (contributes to plaque)
✔ Smoking (accelerates atherosclerosis)
✔ Diabetes (increases inflammation & plaque risk)
✔ Obesity & sedentary lifestyle
✔ Chronic stress & poor sleep
Symptoms of CAD
1. Stable Angina (Most Common Symptom)
- Chest pain/discomfort (pressure, squeezing)
- Triggered by physical/emotional stress
- Relieved by rest or nitroglycerin
2. Unstable Angina (Medical Emergency)
- Occurs at rest or with minimal exertion
- More severe, longer-lasting
- May signal an impending heart attack
3. Heart Attack (Myocardial Infarction)
- Crushing chest pain (may radiate to arm, jaw, back)
- Shortness of breath, cold sweats, nausea
- Requires immediate medical help (Call 911!)
Silent CAD (No Symptoms)
- Some people (especially diabetics) experience no pain
- Detected only via stress tests or angiograms
Diagnosis & Tests
- Electrocardiogram (ECG/EKG) – Checks heart’s electrical activity.
- Stress Test – Monitors heart function during exercise.
- Coronary Angiogram – Gold standard for detecting blockages (uses dye + X-rays).
- CT Coronary Angiography – Non-invasive imaging of arteries.
- Blood Tests – Measure cholesterol, troponin (heart attack marker).
Treatment Options
1. Lifestyle Changes (First Line of Defense)
- Heart-healthy diet (Mediterranean diet, low salt/sugar)
- Regular exercise (150 mins/week of moderate activity)
- Smoking cessation
- Weight management
2. Medications
💊 Statins (lower LDL cholesterol)
💊 Beta-blockers (reduce heart workload)
💊 ACE inhibitors (lower blood pressure)
💊 Aspirin (prevents blood clots)
3. Surgical Interventions
🔹 Angioplasty + Stent – Opens blocked arteries.
🔹 Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG) – Redirects blood flow around blockages.
Preventing CAD
✅ Eat a balanced diet (fruits, veggies, whole grains, lean proteins)
✅ Exercise regularly (walking, swimming, cycling)
✅ Control blood pressure & cholesterol
✅ Avoid smoking & excessive alcohol
✅ Manage stress & sleep well
When to See a Doctor
🆘 Chest pain, shortness of breath, dizziness
🆘 Unexplained fatigue or jaw/arm discomfort
🆘 Family history of early heart disease
Conclusion
CAD is largely preventable with lifestyle changes and early detection. If you have risk factors, consult a cardiologist for screening. A healthy heart starts with daily choices!
For more info:
#HeartHealth #CADAwareness #PreventHeartDisease



