Introduction
Gastric bypass surgery, also known as Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB), is one of the most effective and commonly performed bariatric (weight-loss) surgeries. It helps individuals with severe obesity lose weight by altering the digestive system’s anatomy, reducing stomach size, and bypassing part of the small intestine. This guide covers how it works, who qualifies, benefits, risks, and recovery.
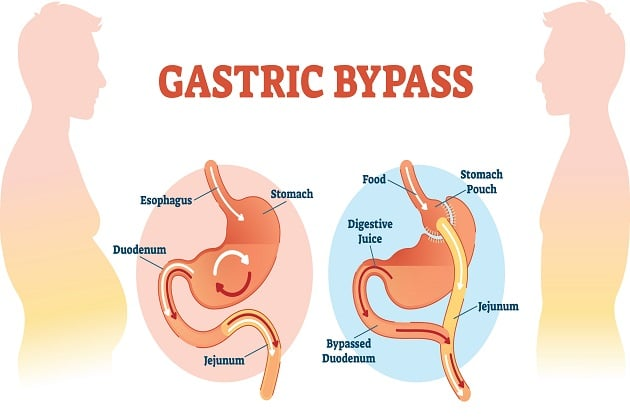
What Is Gastric Bypass Surgery?
Gastric bypass is a restrictive and malabsorptive procedure that:
- Reduces stomach size – Creates a small pouch (about 30 mL) to limit food intake.
- Bypasses part of the small intestine – Reroutes digestion to reduce calorie absorption.
Type of Surgery:
- Usually performed laparoscopically (minimally invasive).
- Takes 2–4 hours under general anesthesia.
- Hospital stay: 2–3 days.
Who Is a Candidate?
Ideal Candidates:
✔ BMI ≥ 40 (severe obesity)
✔ BMI ≥ 35 with obesity-related conditions (e.g., type 2 diabetes, hypertension, sleep apnea)
✔ Failed attempts at weight loss through diet and exercise
✔ Committed to long-term lifestyle changes
Not Recommended For:
❌ Uncontrolled mental health disorders
❌ Severe heart/lung disease
❌ Pregnancy (or planning pregnancy soon)
❌ Inability to follow post-op dietary guidelines
How It Works: The Surgical Procedure
- Stomach Division – The surgeon creates a small pouch at the top of the stomach using staples.
- Intestinal Rerouting – The small intestine is cut and attached to the new pouch, bypassing most of the stomach and part of the small intestine (duodenum and jejunum).
- Reconnection (Roux-en-Y) – The bypassed section is reattached farther down, allowing digestive juices to mix with food.
Result:
- Eat less (smaller stomach restricts food intake).
- Absorb fewer calories (bypassed intestine reduces nutrient absorption).
Benefits of Gastric Bypass
1. Significant Weight Loss
- Lose 60–80% of excess weight within 12–18 months.
- Long-term success – Many maintain >50% weight loss after 5+ years.
2. Improvement in Obesity-Related Diseases
- Type 2 diabetes remission in ~80% of cases.
- Lower blood pressure & cholesterol.
- Reduced sleep apnea symptoms.
- Decreased joint pain & acid reflux.
3. Enhanced Quality of Life
- Increased mobility and energy.
- Improved self-esteem and mental health.
Risks & Complications
Short-Term Risks (Within 30 Days)
- Infection, bleeding, or blood clots (rare but serious).
- Leaks at surgical connections (1–2% risk).
- Dumping syndrome (nausea, sweating after eating sugary/fatty foods).
Long-Term Risks
- Vitamin/mineral deficiencies (iron, B12, calcium – requires lifelong supplements).
- Hernias or bowel obstructions.
- Gallstones (15–20% of patients).
- Weight regain (if diet/exercise habits are not maintained).
Recovery & Post-Op Lifestyle
1. Diet Progression
- Week 1–2: Clear liquids → full liquids (broth, protein shakes).
- Week 3–4: Pureed foods (yogurt, mashed vegetables).
- Month 2+: Soft foods → gradual return to solid foods (small portions).
Key Rules:
- Eat slowly, chew thoroughly.
- Avoid sugary, greasy, or carbonated foods (dumping syndrome risk).
- Prioritize high-protein, low-carb meals.
2. Exercise & Follow-Up
- Start walking immediately after surgery.
- Avoid heavy lifting for 4–6 weeks.
- Regular check-ups (every 3 months in the first year).
3. Lifelong Supplements
- Multivitamin, calcium, iron, B12, and vitamin D (prevents deficiencies).
Gastric Bypass vs. Other Weight-Loss Surgeries
| Surgery | How It Works | Weight Loss | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gastric Bypass | Stomach pouch + intestine bypass | 60–80% excess weight | Effective for diabetes, long-term results | Higher risk of deficiencies |
| Sleeve Gastrectomy | Removes 80% of stomach | 50–70% excess weight | Simpler, no rerouting | Irreversible, less impact on hunger hormones |
| Gastric Band (Lap-Band) | Adjustable band around stomach | 40–50% excess weight | Reversible, least invasive | Slow weight loss, frequent adjustments needed |
Is Gastric Bypass Right for You?
Pros:
✅ Most effective for long-term weight loss.
✅ Improves metabolic health (diabetes, blood pressure).
✅ Covered by many insurance plans if criteria are met.
Cons:
❌ Permanent (not reversible).
❌ Requires strict diet & supplement compliance.
❌ Potential complications if not carefully managed.
Conclusion
Gastric bypass is a life-changing tool for severe obesity, offering dramatic weight loss and health improvements. However, long-term success depends on diet, exercise, and medical follow-up. If you meet the criteria and are ready for a lifelong commitment, consult a bariatric surgeon to discuss your options.



